In this article, we will look at various ways to clean up a disk and free up space on it in any Windows XP, 7, 8.1, 10 operating system.
1. Where does disk space go?
In the process of computer operation, system updates, program installations, website visits and other actions, a lot of junk files often referred to as rubbish or junk. In addition, we often download some files ourselves, and then, when they are no longer needed, we forget about them.
Extra files not only take up disk space, but also reduce system performance. The disk takes longer to search for the necessary files, and some of them may take up space in random access memory and use CPU resources. In addition, viruses often like to sit in temporary files.
Keeping your drive clean and tidy is essential for stable, fast, and reliable computer performance. Now there is also the problem of lack of space for SSD drives, which are very limited.
In this article, we will try to comprehensively solve the problem of lack of disk space. To achieve high results, we recommend that you read the article in full and follow all the tips in the order in which they are presented.
2. Removing unnecessary programs and games
First of all, remove all programs and games you no longer need. This will not only free up disk space, but also speed up the system.
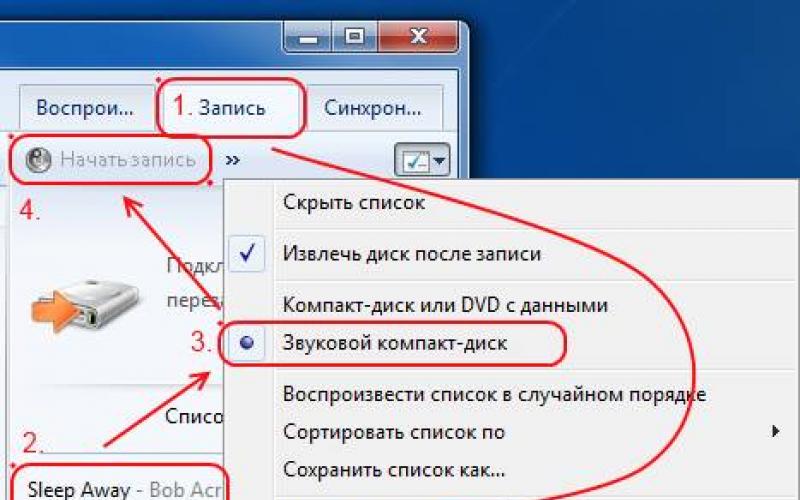
Press the key combination "Win + R", enter "appwiz.cpl" and press "Enter" or use the "Uninstall programs" shortcut from the "" section.
In the window that opens, carefully review the list of programs and games you have installed and remove all that you are unlikely to use in the near future.

To uninstall a program, click on it. right click mouse and select Delete.
Don't delete anything you don't understand the purpose of, or if you're unsure.
After that, manually find and delete the save folders of deleted games, as they can take up a lot of space. It is easy to find out where the saves of a particular game are located by searching the Internet.
Many Online Games also save their distributions (installation packages) during updates that are no longer needed, but at the same time take up a lot of space. For example, the Mail.Ru game center saves distributions in the "Distrib" folder, and the "World of Tanks" game in the "Updates" subfolder. Files in such folders can take up tens of gigabytes and can be safely deleted.
3. Search and delete unnecessary files
It often happens that some old unnecessary files take up a lot of disk space, but we forgot about them and do not know where they are. In order to find them, I recommend using the TreeSize Free utility, which you can download in the "" section.
After launch, the program will scan your disk, determine the sizes of files, folders and sort them by size.

So it will be easy to determine in which folder the files that take up the most space are located. Delete any files you no longer need. If you think you might still need some of them, burn them to disk. The choice of a disk for scanning (C, D, etc.) is made in the "Scan" menu.
4. Transfer user files and folders
If you have a second disk or partition (for example, disk "D"), then first of all transfer all files from the user's desktop and folders such as "My Documents", "My Music", "My Videos", etc. to it ., since they are all physically located on the "C" drive.
You can move files manually by creating folders for them on another disk or partition in advance. But it is more correct to change the location of the user's folders using the operating system. Then all new files that you or some programs will save on the desktop and in the user's folders will automatically go to another disk partition without causing the system partition to overflow.
4.1. Transfer user folders in Windows 7, 8.1, 10
Navigate to the C:\Users\Name folder.

Right-click on the "My Documents" folder and go to the "Location" tab.

Change the drive letter to the one you want to move the folder to (for example, "D") and click OK.

Agree to move the files, and then repeat all the steps for the Desktop folder and the rest of the user's folders.
4.2. Transferring user folders in Windows XP
Windows XP does not have the function of automatically moving user folders and we will use the special XP Tweaker utility, which you can download in the "" section.
Install the utility and run it. Then, in the left pane, select the "Windows XP" section and go to the "System Folders" tab.

Select the "My Documents" folder with the mouse, change the drive letter to the one where you want to move the folder (for example, "D") and click the "Change" button.

Follow the same steps for the folders "My Pictures", "My Music", "Desktop".
After that, go to the folder "C:\Documents and Settings\Name".

And manually move the My Documents and Desktop folders to the new location D:\Documents and Settings\Name.

5. Disk cleanup using Windows
All versions of Windows have a Disk Cleanup feature. With it, you can clean up any partition of the disk (C, D, etc.), but it is most effective for cleaning the system partition (disk "C"), since it is on it that most temporary files are stored.
Right-click on the "C" drive and select "Properties".

Click the "Disk Cleanup" button.

Click the "Clean up system files" button (in Windows 7, 8.1, 10).

Check all the boxes and you will see how much space will be freed up when deleting temporary files.

The volume of temporary files can reach 5-10 GB. Click the "OK" button and all temporary files will be deleted.
6. Deleting the hibernation file
The hibernation file (hiberfil.sys), which can be close to the size of RAM, is located on the "C" drive and is used for sleep mode. If you do not use this mode, but turn the computer on and off every time in the usual way, then this file can be safely deleted, since it takes up a lot of space.
The system will not allow you to delete this file manually, and even if you do it using a special utility for deleting files, the system will create it again. Therefore, in order to correctly delete the hibernation file, you need to disable sleep mode.
Launch command prompt as administrator and run the following command:
Powercfg -h off
After that, the system itself will delete this file and will no longer create it.
If you do not know how to work with the command line or do not want to bother, you can download batch file"Deleting a hibernation file" in the "" section.
You just have to right-click on it and run it as Administrator (except for Windows XP).

7. Disable or resize the paging file
The paging file (pagefile.sys), which can be one and a half times the size of RAM, is located on the C drive and is used by many programs to compensate for the lack of RAM.
With a sufficiently large amount of RAM and a small “C” drive (for example, an SSD), many enthusiasts advise disabling the paging file.
In the window that opens, go to the "Advanced" tab and in the "Performance" section, click the "Options" button.

In Performance Options, go to the Advanced tab and click the Change button.

Uncheck "Automatically select the size of the paging file", check the box "No paging file" and click "OK".

After restarting the computer, the paging file will be deleted and a lot of space will be freed up on the C drive.
But keep in mind that the system is tightly tied to the paging file, and some programs may not have enough even 8 GB of RAM. Therefore, out-of-memory errors may start to appear.

You can try to completely disable the swap file if you have 16 GB or more of RAM, but still I would not recommend doing this.
A-Data Ultimate SU650 120GB Hard Drive8. Disable System Restore
The recovery service does backups system files and stores them in a special hidden folder, which can take up a lot of disk space. At the same time, the built-in recovery tool does not always work correctly, and viruses like to hide in the backup folder.
Press the key combination "Win + R", enter "sysdm.cpl" and press "Enter" or use the "System Properties" shortcut from the "" section.
In the window that opens, go to the "System Protection" tab, select the "C" drive and click the "Configure" button.

Check the "Disable system protection" checkbox and click "OK".

After that, all backup copies of system files will be deleted and additional disk space will be freed up. In this way, you can free up 5-10 GB of valuable space on the "C" drive.
9. Disabling the Recycle Bin
You can disable the recycle bin on the C drive so that it does not take up space on it. To do this, right-click on the trash can icon and select "Properties".

Set the "C" drive to the "Destroy files immediately after deletion" option and click OK.
After that, if you delete large files from folders with game distributions or any others, they will not go to the trash and will not take up space on the C drive.
10. Clean up the backup storage
To clear the backup storage of system files in Windows 8, 8.1, 10, I recommend running the following command on the command line as Administrator.
Dism.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanup
For this purpose, you can also download the "Backup Storage Cleanup" batch file in the "" section and run it as Administrator.

11. Deleting temporary folders
You can painlessly delete temporary folders left after installing some drivers and programs:
C:\AMD C:\ATI C:\CONFIG.MSI C:\Intel C:\MSOCache C:\NVIDIA C:\SWSetup
12. Automatic cleaning and disk acceleration
There are special utilities for automatically cleaning the disk from temporary files. One of the best that I recommend is .
It can be set to clean up temporary files every time you boot your computer, which will keep the C drive free, and also give you a little extra protection, since temporary folders are a favorite place for viruses.
But it is necessary to make its competent configuration, otherwise this utility will clean up not what you need, but what you need to delete will leave. Since the utility settings are quite extensive and it has many additional useful features, I decided to talk about it separately in the next article.
13. Links
A-Data Ultimate SU650 240GB Hard Drive
Hard Drive Transcend StoreJet 25M3 1TB
Hard drive Western Digital Caviar Blue WD10EZEX 1 TB
Almost every PC user sooner or later encounters a situation where drive C (namely, it is usually used for the physical location of the operating system) runs out of space and the system writes “Not enough space on drive C” in the window on the taskbar. Here several questions arise at once: why did the place end and what to do?
If we talk about the first question, the answer is simple: most often the disk space is filled with temporary files. For this reason, I always recommend that you allocate more space for the disk where the operating system. For example, 100 GB will be enough for you even if various programs are located on the same disk. But if you are a fan of powerful games, then there should be at least several times more space, since today games can take up 15-20 GB of free space, and this one is oh so much. In extreme cases, install games on another hard drive.
The answer to the second question is also simple - you need to clear the place. I will show you how this can be done by deleting unnecessary files.
Clearing browser cache
Yes, browsers Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera and Internet Explorer) usually save so many files that you wonder why they are actually needed? Whatever it was, they need to get rid of once and for all.
Clearing the browser cache is very easy. Here, for example, is an instruction for or . In extreme cases, use a program called CCleaner - I wrote about how to use it in one of.

Windows temporary files
Yes, the Windows operating system also has temporary files that are deleted automatically, but this operation is not done as often as we would like. Therefore, we can help Windows get rid of unnecessary files on our own.
If you are using Windows 7 or Vista, then you need to clear the contents of the folders located at the following addresses:
- \Users\Username\AppData\Local\Temp
- \Users\Username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files
- \Users\Username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\History
If you are using Windows XP, then the folder location will be slightly different:
- \Documents and Settings\Username\Local Settings\Temp
- \Documents and Settings\Username\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files
- \Documents and Settings\Username\Local Settings\History
Also, do not forget that folders can be hidden from prying eyes, so they need to be made visible.
Files can be deleted both in the usual way (select files and delete), and using the file manager. The latter is much more convenient to use, besides, he can delete files that cannot be deleted in the usual way.
File upload
Through absolutely any browser, you can download this or that file to your computer. By default, the place where it will be stored is on the C drive. As a rule, most users do not even think about it, and as a result, after a while, a huge number of downloaded files accumulate on the disk.
What to do? To do this, change the location for storing downloaded files. I'll show you on the example of Mozilla Firefox: ideas in the settings and change the path to save files as you wish, approximately as shown in the screenshot:

Do not forget to do the same in if you use it.
Unnecessary programs
Users who have been using a PC for more than the first or even the second year know that initially there is a great desire to install something on the computer, for example, a program for quickly changing wallpaper on the desktop. However, most often the use of the program remains unclaimed, and it takes up space, and sometimes quite a lot. Therefore, we go to the control panel, select the programs that we do not use and remove them. True, you need to remove programs carefully, because due to the removed component, another utility that is associated with it may stop working. Be extremely careful!
Sleep mode
Surprising but true! A few extra gigabytes (!) Can "eat up" the transition to sleep mode! Unfortunately, the system in this case is not perfect, so you can help it become a little better. To do this, go to the power settings through the control panel and disable putting the PC into sleep mode.

Emptying the basket
Most often, I delete files by pressing the Shift + Delete buttons, but the vast majority of users prefer to use the trash in the old fashioned way. And he does the right thing, because in this case, restore deleted files can be done with just one click. But do not forget that the files in the trash take up a lot of disk space, so you need to get rid of them.
Unusually large files
Some programs have the ability to store a huge number of files in the directory where they are located and not delete them at all. For example, some antiviruses are famous for such work, as a result of which the folder size can reach several gigabytes. The easiest way to find such folders is through file manager, which shows their size.
Change the size of the paging file
In system properties, you can also change the size of the paging file used for system operation. It should be noted that reducing the size of this file can adversely affect the operation of the operating system as a whole. However, this will save you a few extra gigabytes.

Windows update files
For older Windows operating systems, the presence of unused folders left after a system update is relevant. As a rule, their name begins with the letter "$", so such folders can be safely deleted. Just be careful not to delete anything important.
Finally, I can’t help but notice that almost no one manually deletes temporary files now. And this makes sense, since third-party programs can do it for you. You don't need to look far for an example - take the same CCleaner. However, the taste and color, as they say ...
There will be questions on the topic of the article, please contact.
So, you are running out of space on your system partition, and you are outraged by the ugly behavior of Windows? Do not rush to blame the operating system, but try to calmly figure out why this is happening.
The lack of space on the system partition is primarily concerned about users who have allocated too little disk space for it. Immediately after installation, modern Windows take up much more space than XP. If you save on matches, you risk making these 6 mistakes!
Let's take a look at the points that most affect the disappearance of disk space.
Swap files and hibernation
Not everyone takes into account that the volumes of RAM installed in computers are growing, and therefore the sizes of paging and hibernation files are growing. In standard configuration windows file swap is 1.5 RAM, and hibernation is 0.75. If you have 8GB of RAM, these two files will take up 18GB immediately after installing the system.
If you do not use all the RAM in your daily work, you can reduce the size of the swap file. On a desktop PC, you can turn off hibernation and use sleep.
Installed programs
Many popular programs have become fairly "fat" in recent years - this also needs to be taken into account (including when determining the size of the system partition).
Remove unused programs (appwiz.cpl) to free up disk space. After removing an unnecessary program, it makes sense to delete its data from folders %AppData% and %LocalAppData% ().
When you install programs, they may copy their installation files to your hard drive so that you can later repair programs or add/remove functionality(and sometimes such copying is done just "just in case"). Unfortunately, there is no supported way to empty the Installer folder.
If you like to test new programs, you will inevitably clog up the system, since the regular removal of the application does not always clean up all the “tails”. For experiments with software it's best to use a virtual machine.
Installed updates
As the operating system is used, free space decreases. When you install updates, the system backs up the files it replaces so that the update can be uninstalled if problems occur. However, modern Windows can delete old copies.
The longer you have worked in the system, the stronger the cleaning effect.
Temporary files of downloaded updates
Downloaded updates are saved to the Windows\SoftwareDistribution folder. Its size does not grow uncontrollably, because the system deletes old files as new ones are downloaded. In the absence of problems, the folder size can reach 700 - 1000MB, and in case of system problems it can be several gigabytes.
To clean up the SoftwareDistribution folder, run a command prompt as an administrator and paste the following code into it.
Net stop wuauserv net stop BITS net stop CryptSvc cd %systemroot% ren SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old net start wuauserv net start bits net start CryptSvc rd /s /q SoftwareDistribution.old
Recovery points
Identify the folders taking up the most space
Use a program that displays the distribution of files on the disk in a graphical form.

Consider NTFS Service Files
NTFS metadata is rarely a significant wastage of space, but it should be included in the calculation. occupied place on disk. On Windows 8 and later, the summary report displays the command
fsutil volume allocationreport C:
Identify the application clogging the disk
Sometimes cleaning helps only for a while, after which the place disappears again as a result of some program running. Knowing the folder where the files are accumulated (see above), you can easily calculate the program.

Make sure there are no viruses
If you followed all the recommendations of the article, but could not find the missing gigabytes, general recommendations are unlikely to help you. In this case, be sure to do a thorough virus scan using a special technique (even if you have an anti-virus program installed and updated regularly).
If nothing helped you, it remains only to advise you to ask a question in the OSZone forum. The article is discussed in this thread.
Ordinary situation. You work at the computer for a long time, not paying attention to the amount of occupied space on local disks, and then the moment comes when there is no space left on the computer at all.
At the same time, someone has one local disk “C”, and someone has 2 of them, even 3, and everyone can be clogged to capacity. But this is not the point, but which folders are usually clogged the most, i.e. which ones should be checked and cleaned immediately.
Because it is usually the main local drive "C" where the system is installed that is subjected to file storming. Unless, of course, the location of some standard folders Windows, such as Downloads, Videos, and other user folders.
And a clogged C drive is not good. Because the system constantly accesses it and the place is needed for the correct operation of its various functions. At least the swap file is written to the C drive, the state of the system is saved there when it is sent to deep sleep (hibernation mode), update files are downloaded and installed.
If the space becomes critically small, this can cause problems in Windows, from slowdowns to major crashes!
A step-by-step plan for finding the most "clogged" folders
There is a way to see through the special program WinDirStatwhich folders and files take up the most space on the computer and where they are located.
Although the program is convenient, not all beginners, despite my instructions for it, will immediately understand how to work with it correctly in order to quickly analyze the structure of files and folders on a computer. Therefore, I propose another option: manually check those main folders that, as a rule, are clogged with users the most. Here's the plan...
1. We look at the size of the system disk "C" and how much space is occupied on it
For starters, if you don't know exactly how big your system drive is and how much space it has already taken, check it out. After all, it may be that your “C” drive is simply initially very small in size, and then the solution should be sought no longer in deleting seemingly unnecessary files, but in increasing the total capacity of the “C” drive, and this is a separate topic.
In this case, follow the steps below to check how much space the main Windows folders(and you can also check it through the WinDirStat program) and if they take up little space, and your disk is almost busy, then it means that your disk is simply of small capacity and all of its space is occupied by the system itself and installed programs.
You cannot change the disk size using standard Windows tools. This can be done, for example, using the program .
Go to the "This PC" section and there, under each disk, its total size and how much free space will be displayed:
Or right-click on the "C" drive (hereinafter referred to as "RMB") and select "Properties":
The General tab will display the disk size (capacity), as well as the amount of used and free space.
Now you can evaluate how busy your C drive is in general and how big it is. And then it may make sense to expand the volume of the disk, and not clean it from unnecessary :)
2. Find folders that often take up the most space
We check in turn the folders of the system user: "Desktop", "Downloads", "Images", "Videos", "Documents", "Music".
It is in these folders that users most often store the bulk of their files and sometimes forget about it. For example, files from the Internet are automatically downloaded to the "Downloads" folder (unless you set another folder through your browser) and many of these files become unnecessary after a while (for example, all kinds of installation files of various programs). And users sometimes forget about this folder, thinking that nothing significant and “heavy” is stored there.
All these folders are located in the user section of the system under which you are working.
To find these folders, go to the local drive "C:" (where your system is installed), open the "Users" folder. There you will see a folder with the name of your user under which you work in the system, for example, I have it "Vladimir".
This folder will display all the user folders that I mentioned above, unless you or someone else has changed their default location.
Alternative ways:

3. Check the size of user folders
Having found the user's folders, we check in turn how much each of them takes up disk space.
To do this, right-click on the folder and select "Properties":
On the "General" tab, in the "On disk" line, the actual size of the space occupied on your local disk by this folder will be displayed. For example, in my example, the Videos folder is 485 GB.
Check all the above user folders in this way and then you will have a picture in front of your eyes: which of these folders are seriously eating up a lot of space on your disk.
4. Check how much space the AppData folder takes up
Windows has a folder where data is being accumulated installed programs on the computer, as well as some system files intended for the user under which you work. This folder is called AppData and is also located on the C drive in your user folder.
To navigate to this folder and check how much space it takes up, you must first turn on the display hidden files and folders (because the AppData folder is initially hidden and you won't see it).
If you do not know how to enable the display of hidden files and folders, then use the information from this article.
After turning on the display of hidden files and folders, go to the "C" drive, open the "Users" folder and then the folder with your user. In it you will see the "AppData" folder:
Through the properties, check its size in the same way as you did with the user's folders. If this folder occupies more than 10 GB, then it will be better to double-check everything in this case, how much each of the folders inside it occupies. Perhaps a folder with some program that you have not been using for a long time, or that has even been deleted from your computer, “eats” a lot of space. Or it's just accumulated temporary files from one of the programs that should have been deleted.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you will surely find a folder or several that are taking up a significant amount of disk space. Then you need to move those folders/files to another local drive or external HDD or delete what you don't need.
Or you will understand that you, in principle, have a very small system disk, which is not enough for normal operation in the system and storing your files. In this case, you need to expand this local disk, as I mentioned above.
For a more accurate analysis of the occupied space, use the WinDirStat program!
If you liked my article, repost it on social networks, leave comments. I will be glad to communicate! :)
If you do not have enough disk space (C:) and as a result, the operating Windows system started to slow down and fail - this article is for you. In it, I collected all the methods for freeing up free space on the system disk that have ever been described on this site.
And I’ll also give you some preventive tips to avoid refilling it to the brim in the future.

So, in the first part of the article, I will raise from the depths of the site all the tips for increasing free space on the system disk, if trouble has already come and it barely moves (almost full to the brim).
Of course, I will not copy here all the texts from the previous articles of the site - I will simply remind the methods and give links to their detailed description.
Methods for increasing free disk space
1. Recommend clean the disk using the built-in system tools. Delete previous Windows versions after her global update if they haven't left your computer yet. Get rid of a large number of unnecessary installers of small updates and programs, from millions of reporting archives and various error logs, temporary files and unnecessary system restore points.
2. Decide on the ones you really need computer programs and delete all other extra or pre-installed by the manufacturer laptop, for example.
You can get rid of programs that are idle and take up disk space in vain with a regular software removal tool or third-party powerful uninstallers.
3. Turn off hibernation, if you do not use it, as well as 90% of all computer users. This step will actually free you up a FEW GIGABYTES on your system drive.
4. Transfer heavy folders of already installed programs to a non-system drive. Only you need to do this not with a simple copy-paste, but special program FreeMove , which will redirect all system calls to them to their new location.
In the same way, you can transfer folders with browser profiles that you have installed - they usually have an impressive size.
Please note: if you have a system SSD drive, and the second one is a regular hard drive, then these folder transfers (browser profiles) can noticeably slow down the work of these programs.
5. If you have enough random access memory- you can disable the paging file in the system properties ...


6. Especially brave (reckless) I advise you to disable the system restore service along with its points. This is if you reinstalling Windows is given easily and quickly (just a buzz) or you know how to revive it with third-party means ...


7. Find the largest files on the disk and delete unnecessary or simply forgotten ones (do not believe it - there will certainly be such).
Remember the proverb: “We are looking for a straw in someone else’s eye, but we do not notice a log in our own”? It's just such a case. 😉
This procedure can be easily and quickly done using special free programs. For example, or.
I’ll give more information about one more and even a download link ...
Low on space on your Windows 10 system drive?
A couple of tips for users current version operating system...
- Windows 10 introduced support for a very powerful, high-quality and safe method compression of individual files and entire program folders - LZX compression. Highly I recommend using it if you don't have enough space on your system drive.
- AT Windows settings 10 find the "Storage" section and activate the "Memory Control" item ...


Actually, this is a very interesting and useful section - you can configure a lot in it to increase free disk space (C :) ...




Let's smoothly move on to preventive actions that will help you keep your system disk clean and always with sufficient free space.
Prevention of free disk space (C:)
1. Transfer the user folders "My Documents", "Downloads" and "Desktop" built into the system to another, non-system drive. This can be done using the method described in this article or using free program FreeMove.
2. Don't forget to always remap your downloads folder in your favorite browsers settings...


If you have not done this before, take all the contents from the default system folder and paste it into a new one. download folder on another drive.